Top Quality AISI52100 GCr15 4mm G10-G1000 Chrome Steel Ball for Motorcycle /Bicycle Parts/ Bearing Ball
Product description

Due to its specific characteristics such as great hardness, high wear resistance, good surface finish and low dimensional tolerances, the low-alloy martensitic AISI 52100 chromium steel is used for the manufacturing of bearings and valves.
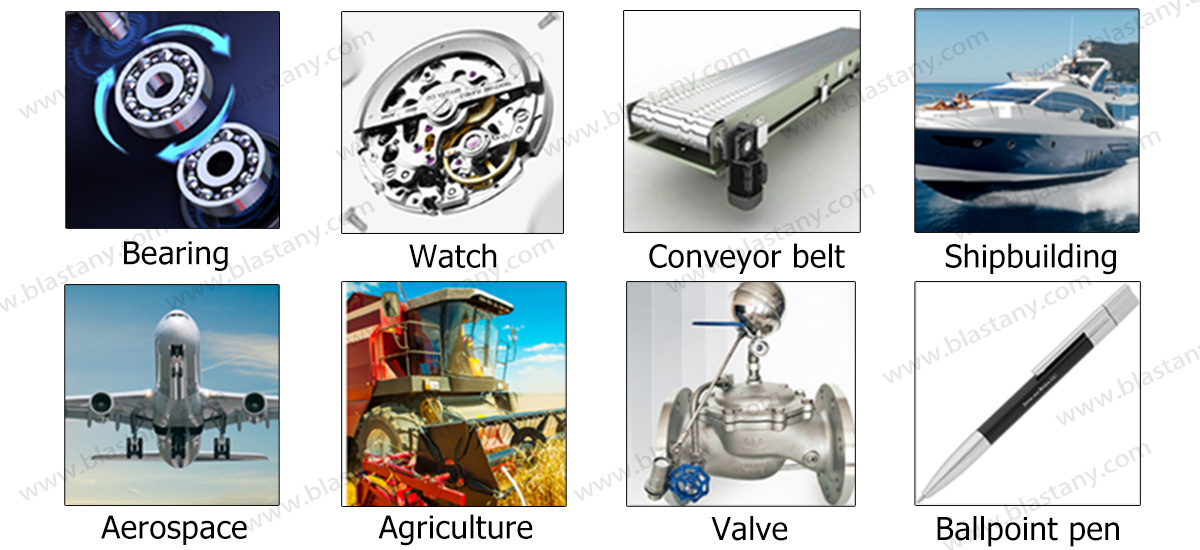
Areas of application
Rolling bearing balls, Valves, quick connectors, precision ball bearings, vehicle components (brakes, steering, transmission), bicycles, aerosol cans, drawer guides, machine tools, lock mechanisms, conveyor belts, slide shoes, pens, pumps, rotating wheels, measuring instruments, ball screws, household electrical appliances.
parameter list
| Chrome Steel Ball | |
| Material | AISI52100/SUJ2/GCr15/DIN 1.3505 |
| Size Range | 0.8mm-50.8mm |
| Grade | G10-G1000 |
| Hardness | HRC:60~66 |
| Features | (1)Comprehensive performance is good. (2)high hardness and uniform. (3)Wear resistance and contact fatigue strength are high. (4)Thermal processing performance is good. |
| Application | Chrome bearing ball mainly used for manufacturing steel balls, rollers and bushings on drive shafts such as internal combustion engines, electric locomotives, machine tools, tractors, rolling equipment, drilling rigs, railway vehicles and mining machinery. |
| Chemical composition | ||||||
| 52100 | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr |
| 0.95-1.05 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.25-0.45 | 0-0.025 | 0-0.020 | 1.40-1.65 | |

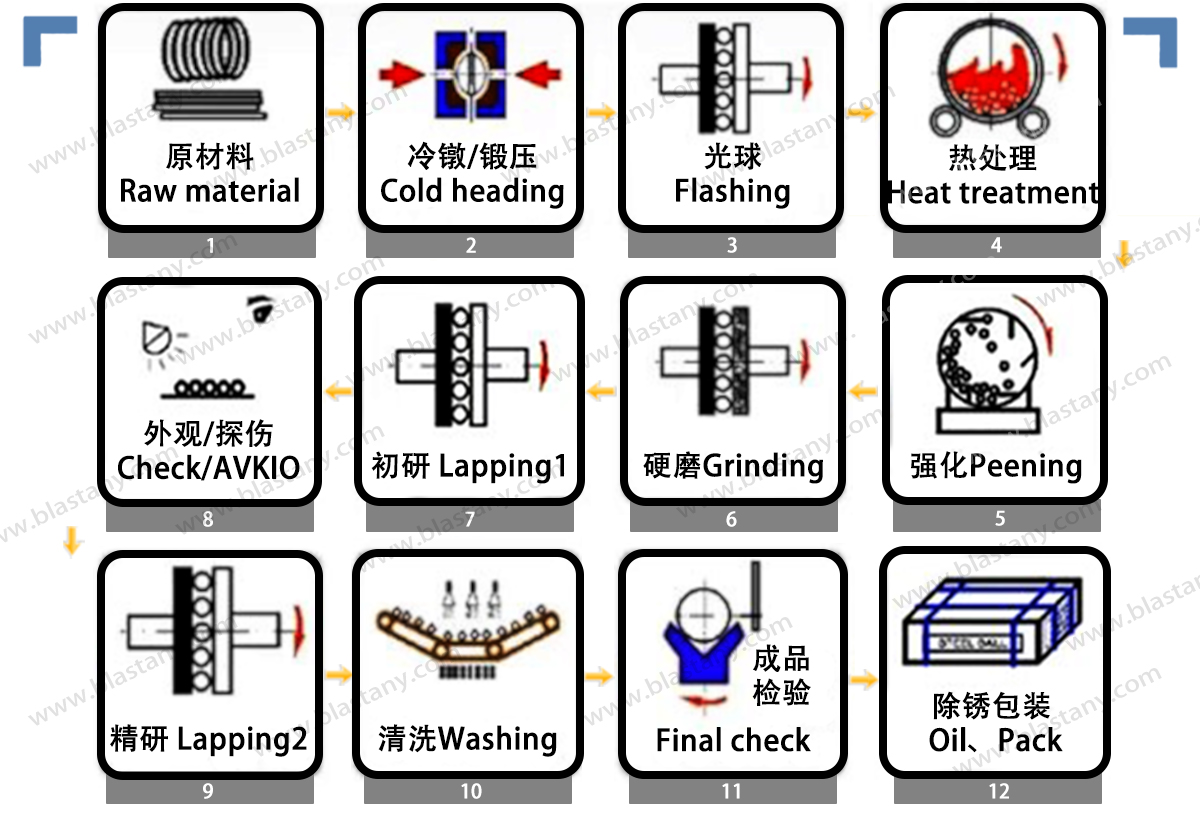
Production process
Raw Material Inspection
Raw material comes in wire form. Firstly, the raw material is visually inspected by quality inspectors to determine if the quality is up to the mark and if there are any defected materials. Secondly, verify the diameter and review raw material certificates.
Cold Heading
The cold heading machine cuts a specified length of the wire material into a cylindrical slugs. After that, the two hemispherical halves of the heading die form the slug into a roughly spherical shape. This forging process is performed at room temperature and a slight amount of additive material is used to ensure that the die cavity is completely filled. Cold heading is performed at very high pace, with an average velocity of one large ball per second. The smaller balls are headed at a speed of two to four balls per second.
Flashing
During this process, the excess material formed around the ball will be detached. The balls are passed a couple of times between two grooved cast iron plates removing small amount of excess material as they roll.
Heat Treatment
The parts are then supposed to be heat treated using quenching and tempering processes.A rotary furnace is used to make sure that all parts bear the same conditions. After the initial heat treatment, the parts are immersed in an oil reservoir. This rapid cooling (oil quenching) produces martensite, a steel phase which is characterized by high hardness and superior wear properties. Subsequent tempering operations further decreases internal stress until the bearings’ final specified hardness limit is reached.
Grinding
Grinding is performed both before and after heat treatment. Finish Grinding (also known as Hard Grinding) brings the ball closer to its final requirements. The grade of a precision metal ball is a measure of its overall precision; the lower the number, the more precise is the ball. Ball grade encompasses diameter tolerance, roundness (sphericity) and surface roughness also called surface finish. Precision ball manufacturing is a batch operation. Lot size is determined by the size of the machinery used for the grinding and lapping operations.
Lapping
Lapping is similar to grinding but has a significantly lower material removal rate. Lapping is done using two phenolic plates and a very fine abrasive slurry such as diamond dust. This final manufacturing process greatly improves surface roughness. Lapping is performed for the sake of high-precision or super-precision ball grades.
Cleaning
A cleaning operation then removes any processing fluids and residual abrasive material from the manufacturing process. Customers who ask for more stringent cleaning requirements, such as those in the fields of microelectronics, medical or food industries, can take advantage of Hartford Technologies more sophisticated cleaning options.
Visual Inspection
After the primary manufacturing process, each lot of precision steel balls undergoes multiple in-process quality control checks. A visual inspection is performed to check for defects such as rust or dirt.
Roller Gauging
Roller gauging is a 100% sorting process that separates both under-size and over-size precision steel balls. Please check out our separate video on the roller gauging process.
Quality Control
Each lot of precision balls is inspected to ensure grade requirements for diameter tolerance, roundness and surface roughness. During this process, other relevant characteristics such as hardness, and any visual requirements are also evaluated.
Products categories











