Coal Based Carbon Raiser Anthracite 92% High Carbon Recarburizer 3-5mm Metallurgical Anthracite Based Carbon Additive

Product Feature
The common types of carburizers in China include Graphitization Carburizing Agent, Calcined Petroleum Coke and Calcined Anthracite Coal,
The raw materials of domestic carburizing agent are heavy oil residue in the process of petroleum refining for coking, namely petroleum coke and asphalt coke. Raw petroleum coke is calcined into calcined petroleum coke. Graphite carburizing agent is obtained by graphitization of raw petroleum coke. Graphitization can reduce the content of impurities, increase the carbon content and reduce the sulfur content.
Carburizing agent is widely used in steel-making, casting, smelting and other industries. The use of carburizing agent in casting can greatly increase the amount of scrap steel, reduce the amount of iron or no pig iron. The carburizing agent can improve the distribution of graphite, promote the graphitization of cast iron, increase the graphite crystal nucleus and fine graphite ball of molten iron, so as to make it more evenly distributed in the matrix and improve the quality of products。
Calcined petroleum coke is mainly used in aluminum industry. In the process of steel-making, Calcined Anthracite Coal can be added as carburizing agent.
Carbon Additive/Carbon Raiser is also called "Calcined Anthracite Coal",or "Gas Calcined Anthracite Coal".
The main raw material is unique high quality anthracite, with characteristic of low ash and low sulfur. Carbon additive has two main uses, namely as the fuel and additive. When being used as the carbon additive of steel-smelting, and casting, the fixed carbon may achieve above 95%.
Best quality Anthracite as raw materials through high temperature calcined at over 2000 by the DC electric calciner with results in eliminating the moisture and volatile matter from Anthracite efficiently, improving the density and the electric conductivity and strengthening the mechanical strength and anti-oxidation, It has good characteristics with low ash, low resistivity, low carbon and high density. It is the best material for high quality carbon products, it is used as carbon additive in steel industry or fuel.
product specification
|
Item |
GPC (Graphitized Petroleum Coke) |
Semi-GPC |
CPC (Calcined Petroleum Coke) |
GCA (Gas Calcined Anthracite) |
GCA (Gas Calcined Anthracite) |
GCA (Gas Calcined Anthracite) |
Graphite Electrode Scraps |
|
Fixed Carbon |
≥ 98.5% |
≥ 98.5% |
≥ 98.5% |
≥ 90% |
≥ 92% |
≥ 95% |
≥ 98.5% |
|
Sulfur Content |
≤ 0.05% |
≤ 0.30% |
≤ 0.50% |
≤ 0.50% |
≤ 0.40% |
≤ 0.25% |
≤ 0.05% |
|
Volatile Matter |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.5% |
≤ 1.5% |
≤ 1.2% |
≤ 0.8% |
|
Ash |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 8.5% |
≤ 7.5% |
≤ 4.0% |
≤ 0.7% |
|
Moisture Content |
≤ 0.5% |
≤ 0.5% |
≤ 0.5% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 1.0% |
≤ 0.5% |
|
Particle Size/mm |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc. |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc |
0–1; 1–3; 1–5; etc |
How to use
1)The use of more than 5 tons of electric furnace, a single stable raw material, we recommend the method of decentralized addition. According to the requirement of carbon content,the carbon additive and the metal charge are added into the middle and lower part of the electric furnace together with each batch. Carbon Additive in the melting do not slag, or easy to wrap in waste slag, affect carbon aborption.
2).Using about 3 tons medium frequency induction furnace, the raw material is single and stable, we recommend the method of centralized adding. When a small amount of molten iron is meted or left in the furnace, the carbon additive should be added to the surface of the molten iron once, and the metal chare should be added immediately, and the carbon additive should be pressed into the molten iron to make the carburizing agent in full contact with the molten iron.
3).using small or medium frequency electric furnace raw material cilo has iron and other high carbon material we recommend carbon additive ine adustment. After Molten steel molten Iron.the carbon content can be adusted and added to the surface of the steel molten iron.The product can be dissolved and absorbed by Eddy current or manual stirring of the steel molten iron during melting in an electric furnace.


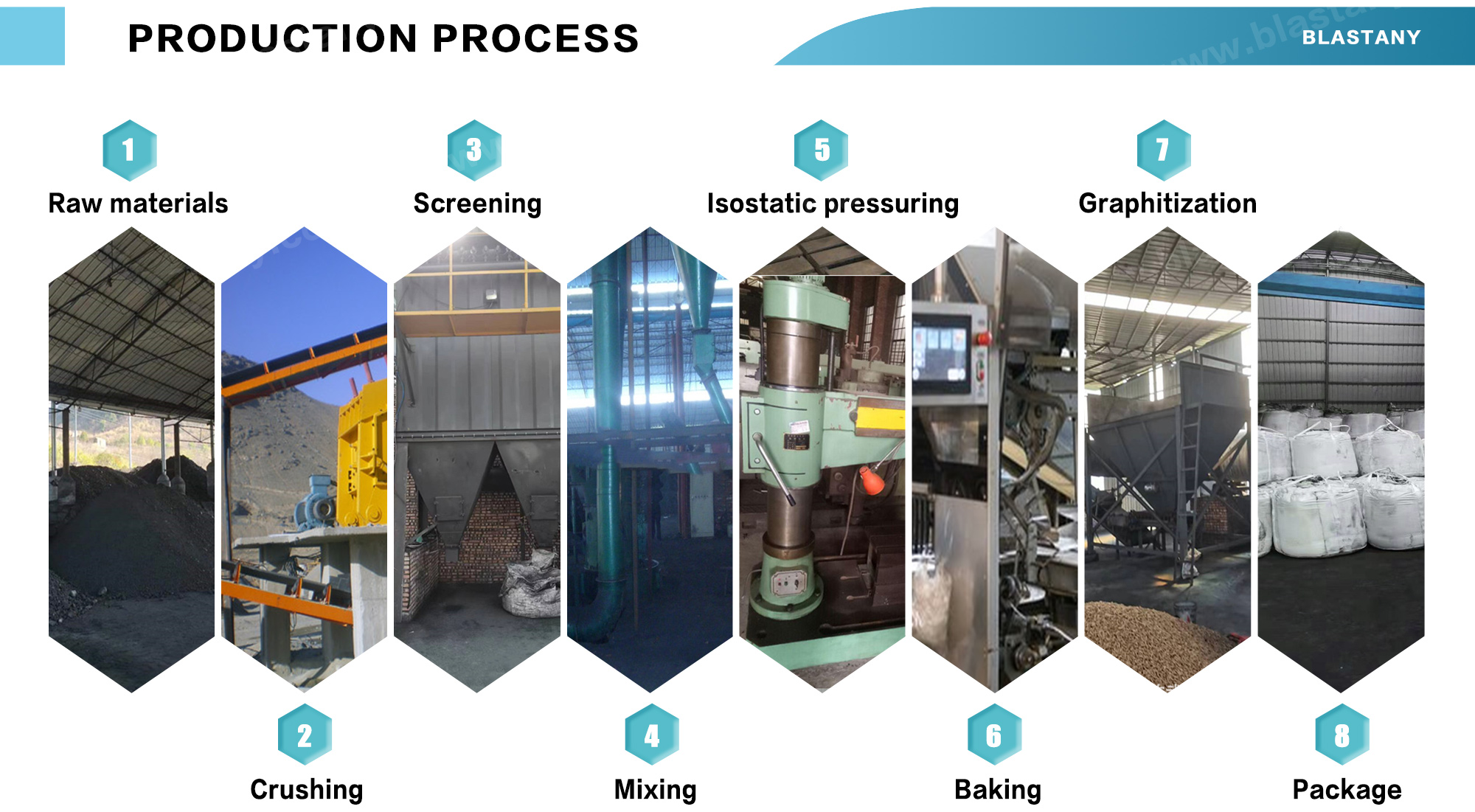
Products categories












